FLS+administrator+guide+7.4.x+_1_.pdf

Materialise Floating License Server
Administrator Guide

Contents
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

1 Introduction
This documentdescribes how to use the Materialise FloatingLicense Server for licenseadministrators.
2 Materialise Floating LicenseServer Overview
TheMaterialise Floating License Server provides the licenses to Materialisesoftware products via a network. The server receivesrequests from the software products,verifies the validity ofrequested license keys and returns the response data.
The floating licenses installedon the server contain the following information:
• Numeric module ID, which identifies the software product’sfunctionality that can beused if this license valid;
• Maximal allowedversion number;
• ![]() Validity period of the license module;
Validity period of the license module;
• Product key (CCKey or voucherkey) the licensemodule is generatedfor; Maximum number ofconcurrent connections.
The main components of the Materialise Floating License Serverare depicted on thefollowing diagram:
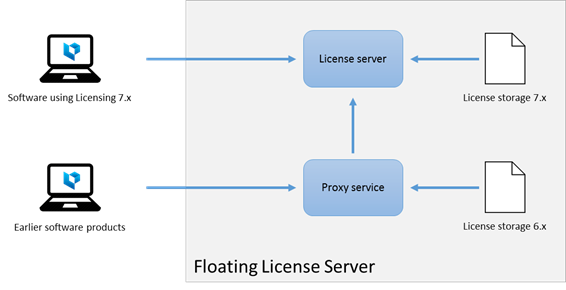 |
The following components are present on the Materialise Floating License Server:
• License server – a service, which processes the license requestsfrom software products, which use the Licensing 7.x component (Magics23 and later software).
• License storage 7.x – a storage, which keeps the license keys used by the License server component.
• Proxy service – a service,which processes the license requestsfrom earlier software products, which do not use theLicensing 7.x components; this proxy service remains for the backwardscompatibility purposes.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

• License storage 6.x - a storage,which keeps the license keys used by the Proxy server component.
2.1. Processing license requestsby Proxy Service
The followinglogic is used by the Proxy Servicewhen processing the license requestsfrom the software products:
1. Forward request to the LicenseServer component.
2. If the LicenseServer can locate the requestedlicense, forward the response to thesoftware product.
3. If the LicenseServer cannot locate the requested licenseat step 1, try to locate it in the License Storage 6.x.
4. Send the responseto the software product.
2.2. 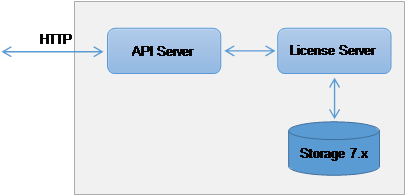 Licensing API Server
Licensing API Server
 |
REST Client
License API Server is a servicethat provides REST-interface for querying licenseserver state (e.g. licensesusage). It acts as a proxy for a License Server exposing its status via HTTP protocol.
License API Server provides/health endpoint for checking API service liveness.
This endpointaccepts GET requestsand replies with 200 status if API Server is workingproperly, 500 otherwise.
License API Server provides/status endpoint for queriying LicenseServer licenses usage.
This endpointaccepts GET requestsand replies with a licensesusage status data structurein a JSON format, which looks like this:
 |
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

![Text Box: "features": [{"name": "string", "totalLicenses": int(64), "usedLicenses": int(64), "type": "string", "sessions": [{"user": "string","host": "string","handle": "string","version": "string", "licenses": int(64)}]}]}] }](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431660/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_12.png)
In defaultconfiguration License API Server returnsall available (non-expired) licenses on the server (features) for a single vendorcalled ‘Materialise Floating License Server’.
Each featureobject contains information about maximum amountof users for a feature,actual current users, license type and lists of current user sessions.
Each sessionobject contains information about user and host name, used featureversion, session handle and amount of used licenses.
Server gives a 200 status code on successful query and 500 on error.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

3 Installing Materialise FloatingLicense Server
3.1. New installation
Installation of the FloatingLicense Server is done with the help of the
FloatingLicenseServer.msi installer package.
1. Start the installation
 |
Press Next to proceedto the next step.
2. Accept the licenseagreement in order to proceedfurther
 |
3. Select the components to install
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

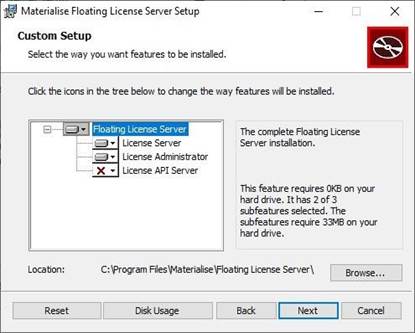
The installation package proposesinstalling the followingcomponents:
- License Server – in this case both the License Serverand the Proxy Service will beinstalled;
- License Administrator – a UI tool,which allows viewing the licensekeys installed on this and other servers, as well asother operations, like registering new license keys;
- License API Server– a server providing REST-interface to query LicenseServer status, licenses usage, etc.
4. Specify the IP port numbers,used by the FLS components.
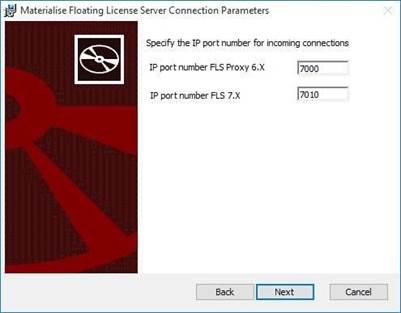 |
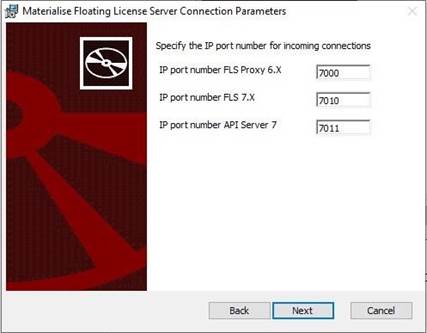
5. When enable LicenseAPI Server you also need to specifyits port.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

6. Confirm selection and proceed to the installation
 |
3.2. Upgrading earlier version
Upgrading the installation of the Materialise Floating License Servercan also be done using the FloatingLicenseServer.msipackage.
When startingthe package on the host, where an earlier versionof the license server is installed, the installer provides auser with the notification about the upgrade.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

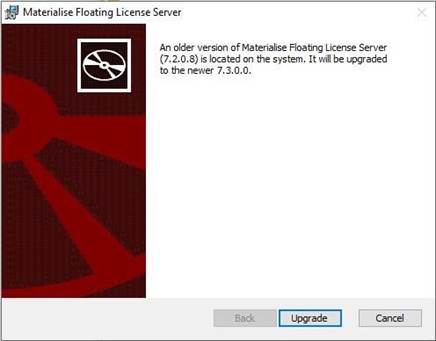
After a user pressesUpgrade, the installation wizard follows the flow describedin the section
3.1. New installation of this document.
3.3. License server components
By default the Materialise Floating License Serveris installed in the following folder:
%PROGRAMFILES%\Materialise\Floating LicenseServer
The following components are installed:
• MatLicenseServer.exe (7.0 subfolder)– the LicenseServer executable file, it is also registered as a WindowsService named “Materialise Floating License Server7”;
• LicSrvFS60.exe –the Proxy Serviceexecutable file, also registered as a Windows Service named “MaterialiseFloating License Server 6.0”;
• LicSrvConfig.exe – configuration UI tool for the Proxy Service component;
• LicAdmin.exe(LicAdmin subfolder) – the LicenseAdministrator UI tool;
• MatLicenseAPIServer.exe (APIServer subfolder) – theLicense API Server executable file, it is also registered as a WindowsService named “Materialise License API Server 7”. This component is installed if LicenseAPI Server feature is enabled.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

4 Managing License Server
4.1. Command line interface
A certainset of operations on the LicenseServer can be done using the commandline interface provided by MatLicenseServer.exe. This sectiondescribes the available commands.
Shows the list of available commandswith a brief description for each.Syntax:
MatLicenseServer.exe -–help
Registers the MatLicenseServer.exe as a “Materialise FloatingLicense Server 7” Windowsservice.
Syntax:
MatLicenseServer.exe –-register MatLicenseServer.exe –r
The commandrequires administrator rights to execute.
Unregisters the “Materialise FloatingLicense Server 7” Windows service.Syntax:
MatLicenseServer.exe –-unregister MatLicenseServer.exe –u
The commandrequires administrator rightsto execute.
Starts the “Materialise FloatingLicense Server 7” Windows service.Syntax:
MatLicenseServer.exe –-start
The command requires administrator rights to execute.
Stops the “Materialise FloatingLicense Server 7” Windows service. Syntax:
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

MatLicenseServer.exe –-stop
The command requires administrator rights to execute.
Please note that the License Servercomponent cannot be stopped withoutfirst stopping the Proxy Service component.
Adds licensekeys delivered in a key file to the licensestorage. Syntax:
MatLicenseServer.exe –-add <path_to_keyfile>
During the execution this command displaysthe progress of adding the modules from the key file:
Shows the system ID value of the host where the license serveris installed. Syntax:
MatLicenseServer.exe –-sysidExample:
4.1.8 Show registered license keys
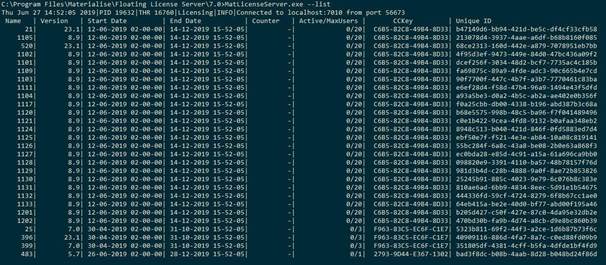
Shows the list of the licensekeys registered on the licenseserver Syntax:
MatLicenseServer.exe –-list
The following data is shown for each key in thelist:
- License module name;
- Maximum allowed versionnumber;
- Validity start date;
- Validity end date;
- Counter (not used);
- Maximum number of users/number of current users;
- CCKey the licensekey has been generated for;
- License key uniqueidentifier (assigned by the licenseserver after registration) Example:
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

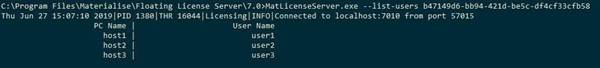
Shows the list of the users and hosts,which are currentlyusing the specifiedlicense key. Syntax:
MatLicenseServer.exe –-list-users <unique_id>
The commandrequires the licensekey’s unique ID as a parameter, it can be obtained via output of the –-list command.
Example:
 |
Deletes a license key from the storage.Syntax:
MatLicenseServer.exe –-delete<unique_id>
The commandrequires the licensekey’s unique ID as a parameter, it can be obtained via output of the –-list command.
Example:
4.2. Configuration file
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
The configuration of the LicenseServer component is defined in thesettings.ini file, which has to be located in the same folder as MatLicenseServer.exe.
If there is no configuration file available at the momentof License Serverstart, it is createdby the server and filled in with default values. In order to applychanges in the file to the License Server, the latter must be restarted.
All valuesin the configuration file are case-insensitive.
The generalconfiguration settings of the LicenseServer component must be definedunder the [general] section in the configuration file.
Below you can find an exampleof the configuration file contentwith the default general settings values.
![Text Box: [general] port=7010 uselogfile=0 loglevel=1logfilepath=C:\ProgramData\Materialise\LicenseFiles\LicenseServer7.log](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431676/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_28.png)
port
The IP port used by the License Serverfor incoming connection. Example:

uselogfile
A flag indicating if the LicenseServer must generatelog file during its work.
logfilepath
Path to the log file createdby the License Server. This parameter is only valid if the
uselogfile parameter is set to 1.
loglevel
The level of log detail(0 – trace, most thorough; 1 – info; 2– warning; 3 – error).Default is 1.
4.2.3 License key access permissions
Materialise FloatingLicense Server allowsconfiguring access permissions to the licensekeys for specific users and hosts.
Access permissions can be configured using white- and blacklist modes:
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

- Blacklist defines the users/hosts, which are not allowedusing the license keys; users, which are not in the blacklist, canuse the requested license key;
- Whitelist defines the users/hosts, which are explicitly allowed using the license keys; users, which are not in thewhitelist, cannot use the requested license key.
Both blacklists and whitelists can be definedfor the following entities:
- Entire server
- Specific licensemodules
- Specific CCKeys
Specificationof a blacklist has a precedence over a whitelist, e.g. if the same user/host islisted in both blacklist and whitelistfor the same entity, the license serverdenies accessing the requestedlicense key.
The following access permission checklogic is used a softwareproduct requests a licensekey:
1. If the user or the hostis in the blacklist for theentire server, access is denied.Otherwise proceed to step 2.
2. If a whitelistis defined for the entire server and neither the user nor the host is in thiswhitelist, access is denied. Otherwise proceed to step 3.
3. If the user or the hostis in the blacklist for the requested module ID, accessis denied. Otherwise proceedto step 4.
4. If a whitelistis defined for the requestedmodule ID and neither the user nor the host is in this whitelist, access isdenied. Otherwise proceed to step 5.
5. If the user or the hostis in a blacklist for the CCKey the requestedmodule belongs to, access is denied. Otherwise proceed tostep 6.
6. If a whitelistis defined for the CCKey the requestedmodule ID belongsto and neither the user nor the host is in this whitelist, access isdenied. Otherwise access is granted.
User and host groupsdefinition
Access permissions to the licensekeys can be configured for specific users, host, but also user and host groups.
Configuration of user groups is done under the [usersgroups] section of the configuration file. Below you can find anexample of defining the user groups named u_group1 and u_group2:
Configuration of host groups is done in a similar way, different section[hostsgroups] is used. Below you can find an example ofdefining the host groups h_group1 and h_group2:
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

Server access permissions
Access permissions to the entire license servercan be defined with the help of settings under the [general] section.
blacklistuseres
The list of users or user groups,which are prohibited from accessing any of the license keys registered on thelicense server.
Example:
![Text Box: [general] blacklistusers=user1, u_group1[usersgroups] u_group1=user101, user102](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431680/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_32.png) |
whitelistusers
The list of users or user groups,which are allowedto use license keys registered on the license server. Users, which are not in this list, areprohibited from using the license keys on the server.
![Text Box: [general]whitelistusers=user1, user2, u_group2 [usersgroups]u_group2=user201, user202](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431681/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_33.png) |
Example:
blacklisthosts
The list of hosts or host groups,which are prohibited from accessing any of the licensekeys registered on the license server.
![Text Box: [general] blacklisthosts=host1, h_group1 [hostsgroups]h_group1=host101, host102](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431682/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_34.png) |
Example:
whitelisthosts
The list of hosts or host groups, which are allowed to use license keysregistered on the license server.Software products on hosts, whichare not in this list, areprohibited from using the license keys on the server.
![Text Box: [general]whitelisthosts=host1, host2, h_group2 [hostsgroups]h_group2=host201, host202](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431683/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_35.png) |
Example:
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

License module access permissions
Access permissions to specifichosts can be defined under the following sections:
- blacklistmoduleusers – definesusers and user groups, which are not allowed using the specified license module;
- whitelistmoduleusers – definesusers and user groups, which are explicitly allowed using the specified license module;
- blacklistmodulehosts – defineshosts and host groups, which are not allowed usingthe specified license module;
- whitelistmodulehosts – defineshosts and host groups, which are explicitly allowed using the specified license module.
In order to define accesspermissions to a specificmodule a setting must be added under one of sections listed above.The name of this settingmust be the respective module ID, the value– a list of the users or hosts in the black- or whitelist respectively.
![Text Box: [usersgroups] u_group1=user101, user102[hostsgroups] h_group1=host101, host102[blacklistmoduleusers] 21=user1, user2, u_group1 22=user3[blacklistmodulehosts] 399=host20, h_group1](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431684/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_36.png) |
Example of blacklist definitions:
![Text Box: [usersgroups] u_group1=user101, user102[hostsgroups] h_group1=host101, host102[whitelistmoduleusers] 21=user1, user2, u_group 22=user3[whitelistmodulehosts] 399=host20, h_group1](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431685/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_37.png) |
Example of whitelist definitions:
CCKey access permissions
Access permissions to specifichosts can be defined under the following sections:
- blacklistproductkeyusers – definesusers and user groups, which are not allowedusing the specified license module;
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

- whitelistproductkeyusers – definesusers and user groups, which are explicitly allowed using the specified license module;
- blacklistproductkeyhosts – defineshosts and host groups, which are not allowed using the specified license module;
- whitelistproductkeyhosts – defineshosts and host groups, which are explicitly allowed using the specified license module.
In order to define access permissions to a specific CCKey a setting must beadded under one of sections listed above. The name of this settingmust be the respective moduleID, the value – a list of the users or hosts in the black- or whitelistrespectively.
![Text Box: [usersgroups] u_group1=user101, user102[hostsgroups] h_group1=host101, host102[blacklistproductkeyusers]C6B5-82C8-49B4-8D33=user1, user2, u_group1[blacklistproductkeyhosts]F963-83C5-EC6F-C1E7=host20, h_group1](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431687/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_39.png) |
Example of blacklist definitions:
![Text Box: [usersgroups] u_group1=user101, user102[hostsgroups] h_group1=host101, host102[whitelistproductkeyusers]C6B5-82C8-49B4-8D33=user1, user2, u_group1[whitelistproductkeyhosts]F963-83C5-EC6F-C1E7=host20, h_group1](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431688/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_40.png) |
Example of whitelist definitions:
TheMaterialise Floating License Server allows reserving certain number concurrentlicenses for certain users or hosts. If a license is reserved in such a way fora user, other users cannot use it and therefore it alwaysremains available for that user. For example, if a license module 21 registered on a license serverhas maximum number of connections 5, and 2 of them are reserved for USER1,other users can only consume 3 remaining connections even if the USER1 is notcurrently using this license module.
The licensereservations can be defined in the configuration file with the help of reservationgroups. Each such group is defined as a section according to the followingformat:
[reservationgroup <group_id>]
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
Each such section can contain settingswith the following names.
modules
Defines the list of modules, which must be reserved.
productkeys
Defines the list of CCKeys,which must be reserved. If the one is defines,all the modules with thisCCKey are reserved for specified users/hosts.
users
Defines the list of users and user groupsthe specified modulesmust be reserved for.
hosts
Defines the list of host and host groupsthe specified modulesmust be reservedfor.
size
The number of connection that must be reserved for specified users and modules. Default value is 1.

In the following example2 connections to the licensemodule 21 are reserved for user1,user2, user101, user102:
![Text Box: [usersgroups] u_group1=user101, user102[reservationgroup r1] module=399users=user1, user2, u_group1 size=2](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431689/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_41.png)
Ifreservations for same license keys are defined in different groups, they addup. For example, license module 21is registered as a part of the CCKey C6B5-82C8-49B4-8D33. Followingreservations are defined:
1. Module 21, 2 connections reservedfor user1, and user2.
2. CCKey C6B5-82C8-49B4-8D33, 3 connections reservedfor user1 and user3.In this case 5 connections will be reserved for user1.
If a reservation group contains both list of users andhosts, this reservation applies to users logged on these hosts.For example, the configuration file contains the following reservation definition:
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

![Text Box: [reservationgroup r2] module=25users=user1, user2 hosts=host1, host2size=2](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431691/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_43.png)
In this case the reserved licensescan be used by:
1. user1 on host1
2. user1 on host2
3. user2 on host1
4. user2 on host2
Extended loggingsettings are configured via the [logger]section. This settingstake precedence over the settings in the [general] section.
Below you can find an exampleof the configuration file contentwith the default logging settings values.
![Text Box: [logger] uselogfile=1 loglevel=1logfilepath=C:\ProgramData\Materialise\LicenseFiles\MatLicenseServer7_logs\Li censeServer_%Y%m%d_%H%M%S_%5N.logrotatelogs=1 logfilerotationsize=134217728 ; 128MB maxtotallogssize=2147483648 ; 2GB minfreediskspace=2147483648 ; 2 GB](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431692/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_44.png) |
UseLogfile
A flag indicating if the LicenseServer must generatelog file during its work.
LogFilePath
Path to the log file createdby the License Server. Supports specifying path as a pattern with counter (%N) and date time (%Y,%m,%d,%H,%M,%S) placeholders
LogLevel
The level of log detail(0 – trace, most thorough; 1 – info; 2– warning; 3 – error).Default is 1.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

RotateLogs
Whether to enable log rotation based on the log filessize.
LogFileRoationSize
The size of the file at which rotationshould occur, in bytes.
MaxTotalLogsSize
The maximumtotal size of log files in folder,in bytes. If the thresholdis exceeded, the oldest file(s) is deleted.
MinFreeDiskSpace
Minimum free space on disk,in bytes. If the thresholdis exceeded, the oldest file(s)is deleted to free space.
HTTPS SSL/TLS settingsare configured via the [ssl] section. Belowyou can find an example of theconfiguration file content with the default settings values.
CipherList
Specifies the supported ciphersin OpenSSL notation(see Appendix A).
Default cipherlist string means using all available ciphers except ciphers containingADH,LOW,EXP,MD5,RC4 and 3DES algorithms; the ciphers are ordered/prioritized by the encryption algorithm key length, soby their reliability.
After updatingthis value the services MatFloatingLicenseServer60 and MatLicenseServer7 require a restart.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

5 Managing Proxy Service
5.1. Command line interface
A certainset of operations on the License Server can be done using the command line interface providedby LicSrvFS60.exe. This sectiondescribes the availablecommands.
Registersthe LicSrvFS60.exe as “Materialise Floating LicenseServer 6.0” Windows service.
Syntax:
LicSrvFS60.exe /r
The command requires administrator rights to execute.
Unregisters the “Materialise FloatingLicense Server 6.0” Windows service.Syntax:
LicSrvFS60.exe /u
The command requires administrator rights to execute.
Starts the “Materialise FloatingLicense Server 6.0” Windows service.Syntax:
LicSrvFS60.exe /start LicSrvFS60.exe /s
The commandrequires administrator rightsto execute. Please note that the Proxy Service
component cannot be startedwithout first startingthe License Servercomponent.
Stops the “Materialise FloatingLicense Server 6.0” Windows service.Syntax:
LicSrvFS60.exe /stop
The command requires administrator rights to execute.
5.2. Configuration UI tool
The ProxyService configuration tool provide evolvedfrom the LicenseServer Configuratorapplication installed next to the license server (both local and floating)version 6.x. At the
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

moment it can only be used to configurethe settings of the Proxy Server, the settings of theLicense Server can be configured via its INI-file.
The configuration tool can be launched with the help of the LicSrvConfig.exe executable file installed next tothe LicSrvFS60.exe.
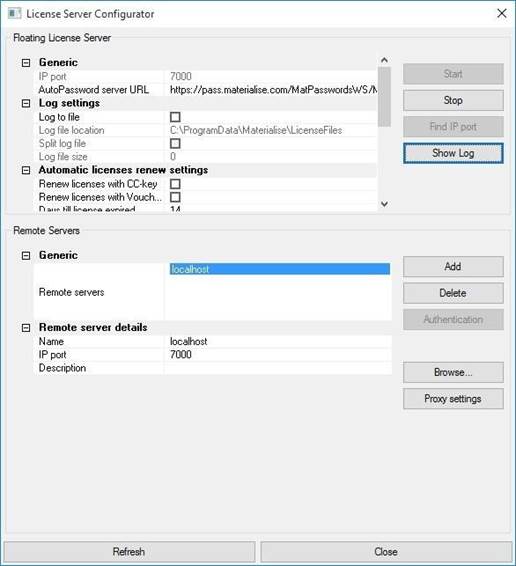 |
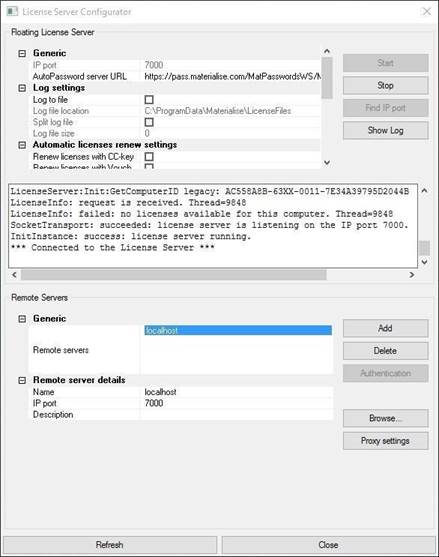
The main screen containstwo major sections:
1. Floating License Server contains the parameters of the ServerProxy.
2. Remote Servers can be used to edit the connections to the licenseservers. These settings are used by the software products installed onthe same host.
This chaptercontains the description of the parameters in the FloatingLicense Server section.
The following control buttonsare available in the FloatingLicense Server section.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

Start
Starts the Proxy Service.The button is disabled if the serviceis already running.
Stop
Stops the Proxy Service.The button is disabled if the serviceis not running.
Find IPport
Automatically finds availableIP port that can be used by the ServiceProxy. The buttonis disable if the service is running.
Show Log
Toggles showing the ServiceProxy log output.
 |
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

IP port
The value of an IP portused by the Proxy Service,the parameter can only be edited if the Proxy Service is stopped.
AutoPassword server URL
The URL of the AutoPassword server, which the Proxy Serviceconnects to when performing the license keysautomatic renewals operation.
This section contains parameters used by the Proxy Servicefor generating the log file.
Log to file
A flag indicating if logging to a file must be turned on.
Log file location
Path to a folderwhere the log file will be created.Only used if the loggingto file is on.
Split log file
A flag indicating if the log file must be split if it reachessome maximum size value.Only used if the logging to file is on.
Log file size
Maximum size of the generatedlog file. If the file becomes bigger,it’s being rolled over.
5.2.4 Automatic licensesrenew settings
This sectioncontains parameters for the automaticrenewal of the license keys using the AutoPassword Service.
Renew licenses with CC-key
Turn the automatic renewalof the license keys generated for CCKeys ON or OFF.
Renew licenses with Vouchers
Turn the automatic renewalof the license keys generatedfor vouchers ON or OFF.
Days till licenseexpired
Number of days before the license key expiration when the auto-renewal will be initiated.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

This sectioncontains the settingsused by the Proxy Serviceto use the license key notification e-mails.
Send e-mail notification
Turn the e-mail notifications ON or OFF.
Days till licenseexpired
The number of days till the licensekeys expiration when an e-mailnotification will be sent. Only used when e-mailnotifications are turned on.
SMTP server
The address of the SMTP server used to send the e-mails.Only used when e-mailnotifications are turned on.
SMTP port
The IP port number on the SMTP server,which is used to send the e-mails.Only used when e-mail notifications are turned on.
Security type
The security type settingfor the SMTP server. Threeoptions are available:
1. No security
2. SSL
3. TLS
Only used when e-mailnotifications are turnedon.
Username
User name requiredto logon to the SMTP server. Only used when e-mail notifications are turned on.
Password
The password requiredto logon to the SMTP server. Only used when e-mailnotifications are turned on.
From
Sender’s e-mail address. Only used when e-mail notifications are turned on.
To Receiver’s e-mail address.Only used when e-mail notifications are turned on.
Subject
Text used as notification e-mailssubject. Only used when e-mailnotifications are turned on.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

6 Managing License API Server
6.1. Command line interface
Acertain set of operations on the License Server can be done using the commandline interface provided by MatLicenseAPIServer.exe. This sectiondescribes the available commands.
Shows the list of available commandswith a brief description for each.Syntax:
MatLicenseAPIServer.exe -–help
Registers the MatLicenseAPIServer.exe as a “Materialise LicenseAPI Server 7” Windowsservice. Syntax:
MatLicenseAPIServer.exe –-register MatLicenseAPIServer.exe –r
The commandrequires administrator rightsto execute.
Unregisters the “Materialise License API Server7” Windows service.Syntax: MatLicenseAPIServer.exe–-unregister MatLicenseAPIServer.exe –u
The commandrequires administrator rightsto execute.
Starts the “Materialise LicenseAPI Server 7” Windows service.Syntax:
MatLicenseAPIServer.exe –-start
The command requires administrator rights to execute.
Stops the “Materialise LicenseAPI Server 7” Windows service.Syntax:
MatLicenseAPIServer.exe –-stop
The command requires administrator rights to execute.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

6.1.6 Restart service
Stops and starts the “Materialise LicenseAPI Server 7” Windows service.Syntax:
MatLicenseAPIServer.exe –-restart
The command requires administrator rights to execute.
6.2. Configuration file
The configuration of the License API Server component locates in the
MatLicenseAPIServer.ini file in the same folder as MatLicenseAPIServer.exe.
Ifthere is no configuration file available at the moment of License API Serverstart, it is created by the server and filled in with defaultvalues. To apply changesin the file to the License API Server, you need torestart the service.
All keys in the configuration file are case-insensitive.
The generalconfiguration settings of the LicenseAPI Server componentare defined under the [general] section in theconfiguration file.
Below you can find an exampleof the configuration file contentwith the default general settings values.
![Text Box: [general] port=7011 uselogfile=1 loglevel=1logfilepath=C:\ProgramData\Materialise\LicenseFiles\LicenseAPIServer7](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431697/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_49.png)
port
The IP port used by the License Serverfor incoming connections.
uselogfile
A flag for enablinglog file generation by the LicenseAPI Server.
logfilepath
Path to the log file to be created by the LicenseAPI Server. This parameter is only valid if theuselogfile parameter is set to 1.
loglevel
Specfies generated log verbosity level. 0– most detailed logs (trace),1 – info, 2 – warning, 3 – only errors. Default valueis 1.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

6.2.3 License Server connection settings
License API Server works as a proxy for License Serverand requires an establishedconnection to work properly. This connection configuration is defined under the[licenseserver] section in the configuration file.
Below you can find an exampleof the configuration file contentwith the default general settings values.
![Text Box: [licenseserver] port=7010 host=localhostvendorname=Materialise Floating License Server](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431698/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_50.png) |
port
The IP port used to connect to the LicenseServer.
host
The hostname used to connect to the LicenseServer.
vendorname
Vendor name of the License Server.Used in the server API model.
Extended loggingsettings are configured via the [logger]section. This settingstake precedence over the settings in the [general] section.
Below you can find an exampleof the configuration file contentwith the default logging settings values.
![Text Box: [logger] uselogfile=1 loglevel=1logfilepath=C:\ProgramData\Materialise\LicenseFiles\MatLicenseServer7_logs\LicenseSer ver_%Y%m%d_%H%M%S_%5N.logrotatelogs=1 logfilerotationsize=134217728 ; 128MB maxtotallogssize=2147483648 ; 2GB minfreediskspace=2147483648 ; 2 GB](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431699/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_51.png) |
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

UseLogfile
A flag indicating if the LicenseServer must generatelog file during its work.
LogFilePath
Path to the log file created by the License Server. Supports specifyingpath as a pattern with counter(%N) and date time (%Y,%m,%d,%H,%M,%S) placeholders
LogLevel
The level of log detail(0 – trace, most thorough; 1 – info; 2– warning; 3 – error).Default is 1.
RotateLogs
Whether to enable log rotation based on the log filessize.
LogFileRoationSize
The size of the file at which rotationshould occur, in bytes.
MaxTotalLogsSize
The maximumtotal size of log files in folder,in bytes. If the thresholdis exceeded, the oldest file(s) is deleted.
MinFreeDiskSpace
Minimum free space on disk,in bytes. If the thresholdis exceeded, the oldestfile(s) is deleted to freespace.
HTTPS SSL/TLS settings are configured via the [ssl]section.
![Text Box: [ssl]certificate=... ; path to file private_key=... ; path to file private_key_password=... ; path to file ca_certificate=... ; path to file verify=falseverification_depth=9cipherlist= ALL:!ADH:!LOW:!EXP:!MD5:!RC4:!3DES:@STRENGTH](https://static.helpjuice.com/helpjuice_production/uploads/upload/image/5908/2431700/Fls_administrator_guide_7.4.x_-_Attachment_52.png) |
certificate
Contains the path to the certificate file (in PEM format).
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

private_key
Contains the path to the privatekey file used for encryption. If empty,default private key file is used.
private_key_password
Contains password to the private key file used for encryption.
ca_certificate
Contains the path to the file or directorycontaining the CA/rootcertificates.
verify
Specifies whether peer verification should be enabled.
verification_depth
Sets the upper limit for verification chain sizes. Verification will fail if a certificate chain larger than this is encountered.
CipherList
Specifies the supported ciphersin OpenSSL notation(see Appendix A).
Default cipherlist string means using all available ciphers except ciphers containingADH,LOW,EXP,MD5,RC4 and 3DES algorithms; the ciphers are ordered/prioritized by the encryption algorithm key length, soby their reliability.
After updatingthis value the services MatFloatingLicenseServer60 and MatLicenseServer7 require a restart.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com

7 Generating license reportswith LicReport Tool
7.1 Introduction
The License serverreporting tool allowsgenerating easy readablereports from aboutthe license server’s work. Below the reporting tool’s workflow isdemonstrated:
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
The License server generates a log file during its work. The log file isread by the LicReport application, its content is analyzed and the resultof the analysis is saved in an XMLfile that can be used for further screening.
Besides the LicReport saves the hardcoded version of the XSL transformation file that can beused for the LicReport.xml for its transformation to the HTML format.
7.2 LicReport usage
LicReport tool comes with the installation of the LicAdmin. Its defaultlocation is C:\Program Files\Materialise\Floating LicenseServer\LicAdmin\LicReport.exe. It can also be delivered as a commandline tool named LicReport.exe, its work is regulated by the command line parameters.
There are three main usage modes: licensemodule usage report,log entries reportand server license list report.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
![]()
7.2.1 License moduleusage report
Thismode is used to generate the output containing the information about theseparate license modules usage duration. By default the XML file named LicReport.xml is generated, its schema is demonstrated below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- edited with XMLSPYv5 rel. 4 U (http://www.xmlspy.com) by Johan Duchateau(Materialise N.V.) -->
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="Report">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Root element</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Generated" type="xs:dateTime">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Date/time when the reportis generated</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Usages">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License usages information</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Module" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Specific module usage information</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="ID" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Module ID</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Name" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Module name</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Version" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Module version</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Type" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License type: 0 - license, 1 - evaluation</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Platform" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License platform:0 - win32, 3 - x64</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Blocks">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Specific module usage blocks</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Usage" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
![]()
<xs:documentation>Module usage block</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Day" type="xs:date">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Date part of the license acquiringmoment</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Time" type="xs:time">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Time part of the license acquiringmoment</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Duration" type="xs:duration">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License usage duration</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Seconds" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License usage duration in seconds</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="TypeEx" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>0 - real license,1 - temporary</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Host" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Host the license is obtained by</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Timeout" type="xs:boolean">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Specifies if the licenseis released on timeout</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Duration" type="xs:duration">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Sum of all the module usage blocks durations</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Seconds" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Sum of all the module usage blocks durationsin seconds</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Duration" type="xs:duration">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Sum of all the license moduleusages</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Seconds" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Sum of all the license moduleusages in seconds</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
![]()
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
The LicReport can analyze log files both for the local and the floatingversion, in the second case itmust run on the same PC where the floating server is installed.
The log file to analyze can be specified using one of two commandline keys:
--find-file [local|floating]
this way the LicReport will try to locate the path to the log file usingthe settings of the respective license server;
--input-file <path>
this way the exactlocation of the log file can be specified.
It is necessary to set one of the keys shownabove, otherwise the LicReport willreturn.
It is also possible to specify the time period for the log entriesto be analyzed using the following keys:
--from-date <yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss>
--until-date <yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss>
If the period is not specified, the entire log file will be used.
The path to the output file can be set usingthe following commandline key:
--output-file <path>
If it is not set, the file named LicReport.xml will be generatednext to the input log file.
It is possible to generatemodule usages in the CSV format by using the --csv-outputkey. The report will contain the following headers by default,: UsageID, ModuleID, Module, Version, Type, TypeEx, Platform, UserName, Host, Day, Time, Duration, Seconds, Timeout. Itis possible to select only specific headers by providing a comma-separatedlist of headers to as a commandargument.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
![]()
Using this mode an XML file will be generatedwith the plain listof the log entries of thefollowing types:
• License check-out
• License check-in
• License request errors
The schema of the output file is demonstrated below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- edited with XMLSPYv5 rel. 4 U (http://www.xmlspy.com) by Johan Duchateau(Materialise N.V.) -->
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="Report">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Root element</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Generated" type="xs:dateTime">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Date/time when the reportis generated</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="LogEntry" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Day" type="xs:date">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The date of the log entry</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Time" type="xs:time">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The time of the log entry</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="ModuleID" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The licensemodule ID operated</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="ModuleName" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The licensemodule name operated</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="ModuleVersion" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The licensemodule version operated</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Host" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The host name the license requestcame from</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="EntryType" type="LogEntryType"/>
<xs:choice>
<xs:element name="EntryGetLicense">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Added if EntryType equalto "GetLicense"</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
![]()
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Type" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License type obtained: 0 - license,1 - evaluation</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="TypeEx" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>0 - real licenseobtained, 1 - temporary one</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Platform" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License platformobtained: 0 - win32, 3 - x64</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="EntryReleaseLicense">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Added if EntryType equalto "ReleaseLicense"</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Type" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License type released: 0 - license,1 - evaluation</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="TypeEx" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>0 - real licensereleased, 1 - temporary one</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Platform" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License platformobtained: 0 - win32, 3 - x64</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Timeout" type="xs:boolean">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Flag specifying if the licensewas released on timeout</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="EntryError">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Added if EntryType equalto "Error"</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Reason" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The error reason</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
![]()
<xs:simpleType name="LogEntryType">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="GetLicense"/>
<xs:enumeration value="ReleaseLicense"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Error"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>
The same commandline keys as for the usage reportare used; the plain list mode is activated using the followingparameter:
--plain-output
By default an XML file named LicReportPlain.xml will be creatednext to the inputlog files unless another output filename is specified using the –output-file key.
This mode generates an XML file containing the list of the licensemodules currently registered on a license server. Both local and floatinglicense servers can be queried,even the floating onesinstalled on remote PCs.
The schema of the output XML is demonstrated below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- edited with XMLSPYv5 rel. 4 U (http://www.xmlspy.com) by Johan Duchateau(Materialise N.V.) -->
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="Report">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Root element</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Generated" type="xs:dateTime">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Date/time when the reportis generated</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="SystemID">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The SystemID for the license server</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Licenses">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="LicenseInfo" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="ID" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License module ID</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="LicVersion" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Module licensing version</xs:documentation>
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
![]()
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Name" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>License module name</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Platform" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Module platform:0 - win32, 3 - x64</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Version" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Module version</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Type" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Module licensetype: 0 - license, 1 - evaluation</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="TypeEx" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>1 for temporary license</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="StartDate" type="xs:date">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Validity period start date</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="EndDate" type="xs:date">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Validity period end date</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="DaysLeft" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Number of days till the expiration date</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="NumUsers" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Number of users the liense is generated for (0 for local licenses)</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="UsageCont" type="xs:integer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Number of users currentlyusing the license</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
The mode is activatedusing the followingcommand line key:
--licence-list [local|floating]
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
![]()
If the floating licenseserver is requested, it is recommended to specify its parameters:
--fls-address <host>
--fls-ipport <ip-port>
If these parameters are not set, the defaultvalues will be used: localhost for the floating server host and 7000 for the IPport number.
The output will be saved in the file named LicList.xml next to the pathto log file of the license server of requested type,unless another locationis specified by the –output-fileparameter.
It is possible to generatemodule usages in the CSV format by using the --csv-outputkey. The report will contain the following headers:ID, LicVersion, Name, Platform, Version, Type, TypeEx,StartDate, Period, DaysLeft,NumUsers, UsageCount. It is possible to select only specific headers by providing a comma-separated list of headers to as a commandargument.
7.3 Command line parameters list
Parameter |
Description |
--help |
Shows help information |
--find-file [local|floating] |
Detects the file location based on the settings of the respective license server (the floating server must be installed on the same PC). If not set, the –input-file key will be used. Ignored if the - -license-list key is set. |
--input-file <path> |
Specifies the path to the log file to analyze. If not set, the –find- file key will be used. Ignored if the --license-list key is set. |
--input-dir <path> |
Specifies the path to the directory with log files to analyze. If not set, the –find-file key will be used. Ignored if the --license-list or --input-file key is set. |
--output-file <path> |
Specifies the path to the output XML file. If it is not set, the output file will be generated next to the input log file. |
--from-date <date time> |
The log entries earlier than this date/time will not be analyzed. If not set, the earliest log entry to be analyzed will be the first one in the log file. Ignored if the --license-list key is set. |
--until-date <date time> |
The log entries later than this date/time will not be analyzed. If not set, the latest log entry to be analyzed will be the last one in the log file. Ignored if the –license-list key is set. |
--plain-output |
Specifies if the plain log entries list must be generated. Ignored if the –license-list key is set. |
--license-list [local|floating] |
The license list registered on the license server specified will be generated. |
--fls-address |
The floating server host to retrieve the license list from. Used only if the –license-list floating is specified. |
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
![]()
--fls-ipport |
The floating server IP port to retrieve the license list from. Used only if the –license-list floating is specified. |
--no-xsl |
Turns off the generation of the hardcoded XSL files. |
--csv-output [csv headers] |
Turns on generation of the report in CSV format. |
--skip-orphans |
Enables skipping orphaned log events (reserve without release and vice versa). |
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
![]()
Appendix A: CipherList Format
The cipher list consists of one or more cipherstrings separated by colons. Commas or spaces are also acceptableseparators but colons are normally used, e.g.:
ALL:!ADH:!LOW:!EXP:!MD5:!RC4:!3DES:@STRENGTH
The actual cipher string can take severaldifferent forms. It can consist of a singlecipher suite such as RC4-SHA.
It can representa list of cipher suitescontaining a certainalgorithm, or ciphersuites of a certain type. Forexample SHA1 represents allciphers suites using the digest algorithm SHA1 and SSLv3 represents allSSL v3 algorithms.
Lists of ciphersuites can be combined in a singlecipher string using the + character. This is used as a logical andoperation. For example SHA1+DESrepresents all cipher suites containing the SHA1 and the DESalgorithms.
Each cipherstring can be optionally precededby the characters !, - or +.
If ! is used then the ciphers arepermanently deleted from the list. The ciphers deleted can never reappear inthe list even if they are explicitly stated.
If - is used then the ciphers are deletedfrom the list, but some or all of the ciphers can be added again by lateroptions.
If + isused then the ciphers are moved to the end of the list. This option doesn'tadd any new ciphers it justmoves matching existing ones.
If none of these characters is present then the string is just interpreted as a list of ciphers to be appended to the currentpreference list. If the list includes any ciphers alreadypresent they will be ignored:that is they will not moved to the end of the list.
The cipher string@STRENGTH can be used at any point to sort the currentcipher list in order of encryption algorithm keylength.
The cipher string@SECLEVEL=n can be used at any point to set the securitylevel to n, which should be a number between zero and five, inclusive. See SSL_CTX_set_security_level for a description of what each level means.
The cipher list can be prefixed with the DEFAULT keyword, which enables the default cipher list as definedbelow. Unlike cipher strings, this prefix may not be combined with otherstrings using + character. For example, DEFAULT+DES is not valid.
The content of the default list is determined atcompile time and normally corresponds toALL:!COMPLEMENTOFDEFAULT:!eNULL.
Materialise nv I Technologielaan 15 I 3001 LeuvenI Belgium I info@materialise.com I materialise.com
